3D printing is an incredible technological tool both in and out of the medical world. Fortunately, this revolutionary technology has opened up an entirely new realm of possibilities for medical professionals to better their patient’s care.
Why Is 3D Printing Important To Medical Professionals?
3D printing has enabled doctors to create models of patients’ organs, tissues, and bones that can show the precise image of the patient’s anatomy, enabling them to make more thorough and accurate diagnoses. This means that diseases can be caught faster, leading to a higher percentage rate of positive outcomes.
These models are helpful to ensure quality by using test treatments on a physical model before trying them on a patient. This can help to reduce the risk of adverse reactions and ensure that the treatment is as effective as possible. In addition, 3D printing can be used to create prosthetic limbs, allowing patients to receive a personalized prosthesis that is custom fit to their body.
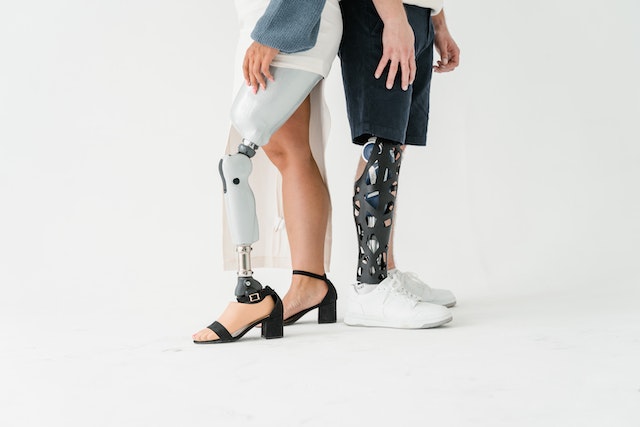

Finally, 3D printing is being used to create custom medical implants. Medical implants are used to replace missing or damaged tissue. They are typically made of titanium or other materials, but 3D printing has enabled medical professionals to create custom implants that are specifically designed for each patient. This has improved patient outcomes and allowed doctors to create implants that are more effective than ever before.
3D Printing In Radiology
In an interview for the American College of Radiology, Kenneth C. Wang, MD, Ph.D. said, “the benefit of printing comes from the patient-specific nature of what is depicted. And that almost always starts with imaging. That’s why we, as radiologists, are so well positioned to be at the center of these workflows. We can use our deep understanding of imaging modalities, anatomy, and disease to create models, interpret findings and also to know the limitations of the images, and communicate with other providers.”
3D printing has become an increasingly common and useful tool for radiologists. Because it can be used to create customized models of organs, bones, and other body parts, it gives radiologists a better visualization and understanding of medical conditions that couldn’t be seen before. The in-depth imaging 3D printing provides can also be used to create medical implants, such as scaffolds for bone regeneration and customized joint replacements.
3D-printed models of organs can be used to practice minimally invasive procedures and to create guides for surgeons to follow during operations.
This will help with medical education, allowing students and radiologists to visualize the anatomy and better understand medical conditions. Finally, 3D printing can be used to create patient-specific medical devices, such as hearing aids and prosthetics, to customize them and make them more comfortable for patients.
Conclusion
Overall, 3D printing has revolutionized the world of radiology. It has allowed medical professionals to make more precise and accurate diagnoses, create custom medical devices, create models of organs, tissues, and bones, and create custom medical implants. This technology has enabled doctors to provide better patient care and has improved patient outcomes. With this kind of technology coupled with Artificial Intelligence, the sky is the limit.
Vesta Teleradiology is always looking to new technologies to improve our operations and further assist our clients in accurate and quick interpretations. Please reach out to us to learn about how we customize the process for your healthcare facility’s needs.