Elevating Radiology. Expanding Access. Enhancing Care.
Vesta Teleradiology is redefining radiology delivery by integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into our diagnostic and operational workflows – helping hospitals of every size achieve higher quality, faster turnaround, and greater consistency in patient care.
Through our newly launched partnerships with Qure.ai and Carpl.ai, Vesta is bringing the benefits of AI assisted imaging to both large health systems and rural or underserved communities across the nation. This innovation enhances the speed, accuracy, and accessibility of radiology services – ensuring clinical excellence reaches every patient, everywhere.
AI Partnerships Driving Clinical Quality and Efficiency
Vesta now integrates Qure.ai’s FDA cleared AI solutions directly into our reading workflow to support both CT and X-ray imaging. For CT Brain (Non-Contrast), the AI automatically detects intracranial hemorrhages, fractures, and mass effect to improve triage and accelerate emergency response times. For Chest X-rays, it identifies nodules, effusions, and acute pulmonary findings to strengthen diagnostic consistency and enable earlier intervention. These tools work as a co-pilot for radiologists – helping prioritize critical studies, standardize interpretations, and deliver higher-quality reports with precision and speed.
Vesta also leverages Carpl.ai’s enterprise grade AI platform for musculoskeletal (MSK) fracture detection, enabling faster identification of subtle skeletal injuries that are often missed under high volume workloads. This integration enhances both radiologist efficiency and patient safety by improving consistency, turnaround times, and workflow throughput.
Expanding AI Across Vesta’s Clinical and Operational Ecosystem
In addition to our partnerships with Qure.ai and Carpl.ai, Vesta continues to implement AI across the organization to enhance both clinical quality and operational efficiency. Through RadPair, Vesta improves dictation accuracy, peer review workflows, and reporting analytics for radiologists – driving consistency and precision across the reading process.
On the operations side, Vesta has developed and launched an AI based support platform that allows staff to instantly retrieve internal protocols, radiologist schedules, credentialing data, and study specialty details from a centralized location. These tools streamline communication, improve turnaround time, and strengthen coordination across departments – supporting faster, more efficient service for clients and radiologists alike.
AI with a Purpose: Clinical Quality Care for All
Vesta’s mission has always been clear – to combine technology, compassion, and clinical excellence to improve access to quality radiology care. By implementing these AI partnerships and innovations, we’re ensuring faster turnaround for emergent and high acuity studies, improved diagnostic accuracy through validated AI support, greater access for rural and underserved hospitals, and consistent quality across every facility, 24/7/365.
These advancements reaffirm Vesta’s leadership as a trusted partner in AI driven radiology innovation, bringing cutting edge technology to the frontlines of patient care while optimizing the systems that support it.
About Vesta Teleradiology
Vesta Teleradiology is a Joint Commission-Accredited, 24/7/365 radiology provider serving hospitals, imaging centers, and healthcare systems nationwide. Our team of board-certified radiologists delivers timely, accurate, and secure interpretations – now further enhanced by AI technology to support faster decisions, higher quality, and better outcomes.
Interested in learning how Vesta’s AI powered radiology can support your hospital or health system?
Contact us at info@vestarad.com or visit www.vestarad.com/contact to schedule a demo or consultation.
Attribution:
Vesta Teleradiology integrates third party AI technologies through collaborations with Qure.ai, Carpl.ai, and RadPair. Descriptions of imaging and workflow capabilities in this publication are based on publicly available clinical use cases and are provided for informational purposes only. All content and messaging on this page are original to Vesta Teleradiology.

 From Quantitative Imaging to Clinical Translation
From Quantitative Imaging to Clinical Translation

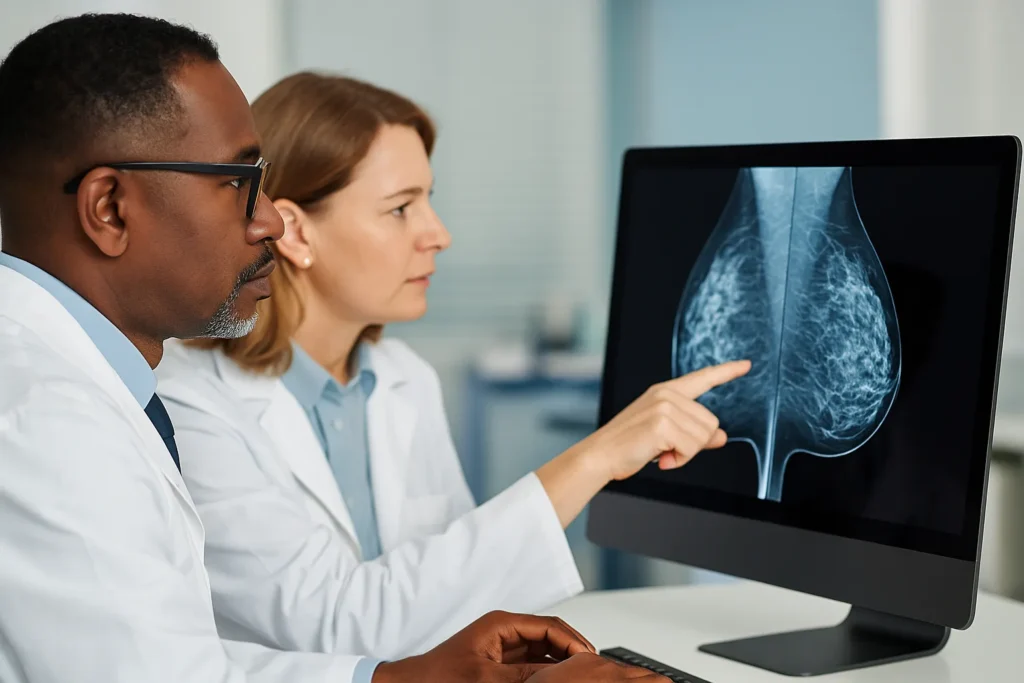 New trial evidence favors MRI and contrast-enhanced mammography
New trial evidence favors MRI and contrast-enhanced mammography




 The Growing Demand for Subspecialty Reads
The Growing Demand for Subspecialty Reads
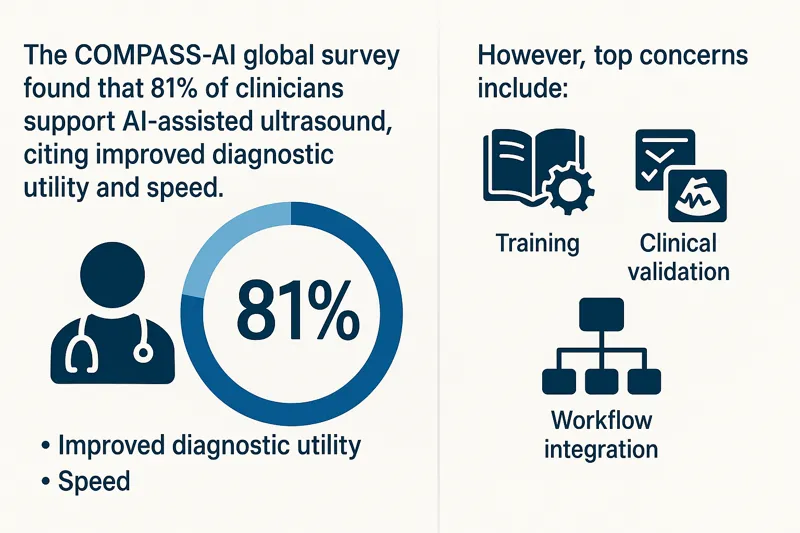 Why It Matters for Facilities and Radiology Teams
Why It Matters for Facilities and Radiology Teams